

Full support for Microsoft DirectX 9.0 Shader Model 3.0 enables stunning and complex special effects. 2nd-generation technology delivers more than 4x the shadow processing power over the previous generation.Integrated HDTV Encoder provides world-class HDTV-out functionality up to and including 1920x1080i resolutions.By combining the incredible dynamic range of today's state-of-the-art 3D motion pictures with 128-bit studio-precision color, the GeForce FX GPUs bring you the industry's best image quality for the most demanding applications.Superscalar 24-pipe GPU architecture delivers up to 2x the shading power of previous generation products taking gaming performance to extreme levels.NVIDIA CineFX 4.0 Engine delivers advanced visual effects at unimaginable speeds. The GeForce 7800 GTX graphics processing units (GPUs) deliver the revolutionary technologies and an unmatched feature set for high-performance gaming.UltraShadow II technology enhances the performance of bleeding-edge games, like id Software's Doom III, that feature complex scenes with multiple light sources and objects.The introduction of the GeForce GTX 295 with two GT200 cores in 2009 further cemented the market position of the 200 series. It could not cleanly outperform the GeForce 9800 GX2, but because the 9800 GX2 had considerably higher power consumption and less memory, the GTX 280 was still considered the superior graphics card. The GT200 launched in the Nvidia GeForce GTX 280, which was significantly faster than the GeForce 9800 GTX+ due to the increased resources. The memory bus was extended from a 256-bit interface to a 512-bit wide connection to the GDDR3 memory pool. Nvidia also doubled the number of ROPs from 16 in the G92 to 32 in the GT200. Whereas the G92 had eight Texture Processor Clusters (TPC) with 16 EUs and eight TMUs, the GT200 used ten TPCs with 24 EUs and eight TMUs each. Changes made to the architecture included an improved scheduler and instruction set, a wider memory interface, and an altered core ratio. Nvidia introduced the GT200 core based on an improved Tesla architecture in 2008.
#OPENGL WINDOWS 10 NVIDIA 7800 GTX SERIES#
G92 And G92B: GeForce 9000 Series (Continued) The card was also considerably more expensive than the 8800 Ultra, which made it a tough sale. Each G92 on the 9800 GX2 had access to 512MB of GDDR3, while the 8800 Ultra came with 768MB. When AA was active, however, the 9800 GX2's performance lead shrunk to 13% due to RAM limitations. In tests, the 9800 GX2 outperformed the 8800 Ultra on average between 29 to 41% when AA was turned off. This was something Nvidia was unable to do with the power-hungry G80. Thanks to the improved energy efficiency and reduced heat, Nvidia launched a dual-G92 GPU called the GeForce 9800 GX2 as the flagship in the 9000 series. By fabricating G92 at 65 nm, Nvidia was able to hit clock speeds ranging from 600 to 675 MHz all while reducing overall power consumption. Nvidia's G92 core inside the 9000-series flagship was essentially just a die shrink of G80. Nvidia continued to use the Tesla architecture in its GeForce 9000 series products, but with a few revisions. G92: GeForce 9000 Series And Tesla Improved Although both graphics cards used the same G80 core, the 8800 Ultra was clocked at 612 MHz, giving it a slight edge over the 8800 GTX. All of these enhancements allowed the GeForce 8800 GTX perform more than twice as fast as its predecessor in high-resolution tests.Īs yields improved, Nvidia later replaced the 8800 GTX with the 8800 Ultra as the flagship.
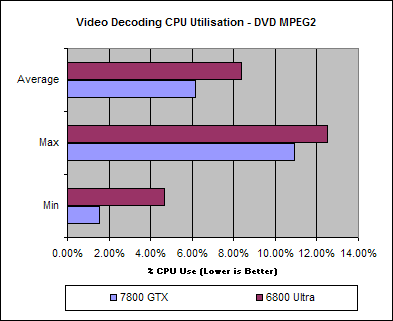
Nvidia also increased the number of TMUs up to 64 and raised the ROP count to 24. The 8800 GTX came with 128 shaders clocked at 575 MHz and connected to 768MB of GDDR3 over a 384-bit bus. Thanks to the unified shader architecture, the 8800 GTX and the rest of the 8000 series featured full support for Microsoft's new DirectX 10 API and Pixel Shader 4.0. The GeForce 8000 series's flagship was the 8800 GTX, powered by Nvidia's G80 GPU manufactured at 80 nm with over 681 million transistors. Tesla would become one of Nvidia's longest-running architectures, as it was used inside the GeForce 8000, GeForce 9000, GeForce 100, GeForce 200, and GeForce 300 series of GPUs. Nvidia introduced its Tesla microarchitecture with the GeForce 8000 series - the company's first unified shader design.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
